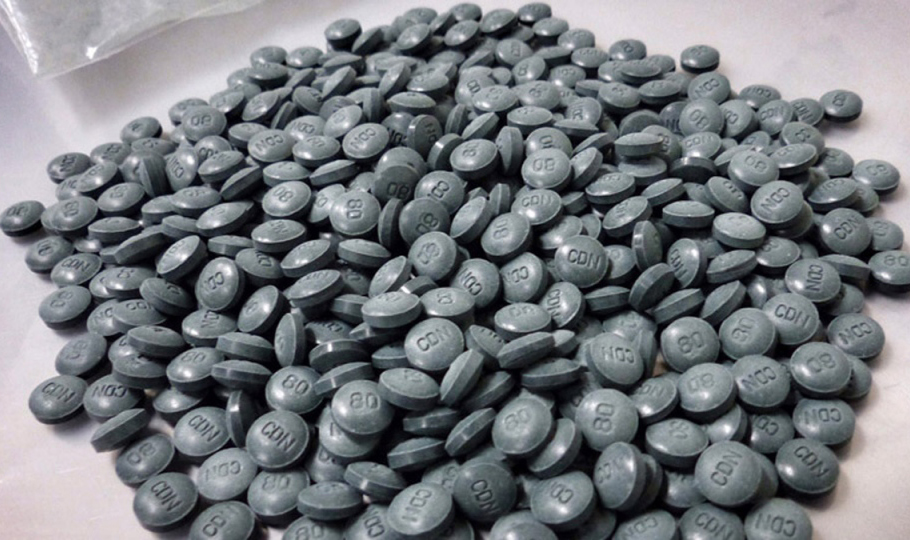
 Fentanyl is a powerful synthetic opioid that is similar to morphine but is 50 to 100 times more potent, according to the National Institute on Drug Abuse. Used to treat pain, it is categorized as a Schedule II drug and carries a “black box warning” from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to call attention to its serious and life-threatening risks. Illegally-made, fentanyl is frequently mixed with heroin to become more powerful, and unfortunately, both users and dealers are unaware of the actual contents of the product.
Fentanyl is a powerful synthetic opioid that is similar to morphine but is 50 to 100 times more potent, according to the National Institute on Drug Abuse. Used to treat pain, it is categorized as a Schedule II drug and carries a “black box warning” from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to call attention to its serious and life-threatening risks. Illegally-made, fentanyl is frequently mixed with heroin to become more powerful, and unfortunately, both users and dealers are unaware of the actual contents of the product.
The United States is experiencing a sharp increase in the abuse and theft of fentanyl. The U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) has issued multiple nationwide warnings about the dangers of fentanyl alongside health alerts from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). In March 2015, DEA administrator Michele M. Leonhart said, “Drug incidents and overdoses related to fentanyl are occurring at an alarming rate throughout the United States and represent a significant threat to public health and safety.” More recently, the DEA released a video for law enforcement explaining that just touching fentanyl can result in absorption through the skin, and inhalation of the powder while it’s airborne can be deadly.
Here are some alarming statistics surrounding fentanyl and drug overdose:
- The DEA reports that the current outbreak involves fentanyl and fentanyl compounds which has resulted in thousands of deaths in a wide geographic area.
- According to data from the National Forensic Laboratory Information System (NFLIS), confiscations and seizures of fentanyl increased nearly seven-fold from 2012 to 2014.
- The CDC said, “Recent fentanyl-related fatal overdose data from several of the top 10 states with highest seizure counts suggest fatalities have increased in states reporting large increases in fentanyl seizures.”
- USA Today reported that clandestine labs in China are producing fentanyl that is being trafficked into the U.S. by Mexican drug dealers.
- Drug overdose is now the leading cause of accidental death in the United States. Fatal overdoses from opioid medications have quadrupled since 1999, accounting for more than 28,000 deaths in 2014
Quest Diagnostics offers drug testing solutions that screen for illicit drugs such as heroin as well as prescription drugs. Our expanded opiates panel and specialty test panels can be used to detect narcotics such as fentanyl and other opioids such as oxycodone, hydrocodone and methadone.
Download our free reference guide for Common Drugs of Abuse.
To learn more about drug testing, visit our website.
 Your Privacy Choices
|
Privacy Notices
|
Terms
|
Language Assistance / Non-Discrimination Notice | Asistencia de Idiomas / Aviso de no Discriminación | 語言協助 / 不䈚視通知
Your Privacy Choices
|
Privacy Notices
|
Terms
|
Language Assistance / Non-Discrimination Notice | Asistencia de Idiomas / Aviso de no Discriminación | 語言協助 / 不䈚視通知


















The United States is experiencing a sharp increase in the abuse and theft of fentanyl. The U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) has issued multiple nationwide warnings about the dangers of fentanyl alongside health alerts from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). In March 2015, DEA administrator Michele M. Leonhart said, “Drug incidents and overdoses related to fentanyl are occurring at an alarming rate throughout the United States and represent a significant threat to public health and safety.” More recently, the DEA released a video for law enforcement explaining that just touching fentanyl can result in absorption through the skin, and inhalation of the powder while it’s airborne can be deadly.
Here are some alarming statistics surrounding fentanyl and drug overdose:
Quest Diagnostics offers drug testing solutions that screen for illicit drugs such as heroin as well as prescription drugs. Our expanded opiates panel and specialty test panels can be used to detect narcotics such as fentanyl and other opioids such as oxycodone, hydrocodone and methadone.
Download our free reference guide for Common Drugs of Abuse.
To learn more about drug testing, visit our website.